Virology
VIROLOGY is the study of Viruses. VIRUSES are microscopic infectious agents that are unable to reproduce outside of a host organism. As a result they rely on the host organism for their replication and survival. The general structure of a virus is a protective protein coat, the capsid, which encloses the genetic material, and either DNA or RNA. Viruses are responsible for numerous human diseases usually named after the virus (e.g. HIV infected individual).
In our laboratory we perform a variety of virology tests towards detecting:
Hepatitis Virus B (HBV)
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Hepatitis Virus C (HCV)
Epstein Bar Virus (EBV)
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
Syphilis

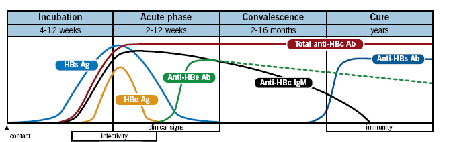
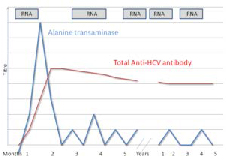
These viruses have distinct characteristics as the disease progresses allowing us to
determine the presence and the progression of the disease. For instance the graphs
below show the different antigens and antibodies produced by HBV and HCV viruses
(Figs 1 and 2 respectively) during the different phases of infection. It might be useful to
use this graph when a Hepatitis profile is requested.
VIROLOGY
- Hepatitis B Surface
- Antigen (HBsAg)
- Hepatitis Bs antibody (Anti-HBs)
- Hepatitis B Core IgG
- Antibodies (AntiHBcIgG)
- Hepatitis C Antibodies (Anti-HCV)
- Human Immunodeficiency
- Virus (HIV)
- Cytomegalovirus IgG (CMV IgG)
- CMV IgM
- Epstein Barr Virus IgG (EBV IgG)
- EBV IgM
- Venereal Disease Research
- Laboratory test
(VDRL)
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (HBsAg)
- Hepatitis B Core IgG
- Antibodies (AntiHBcIgG)
- Hepatitis B Core IgM
- Antibodies (AntiHBcIgM)
- Hepatitis Be Antigen (HBeAg)
- Hepatitis Be Antibody (Anti-HBe)
- Hepatitis Bs antibody (Anti-HBs)
Useful Websites for additional Information:
-
American Foundation for AIDS Research
Visit American Foundation for AIDS Research website for more details
-
National Institutes of Health – Hepatitis
For general information on hepatitis viruses, visit the website
-
National Institutes of Health – Sexually transmitted diseases
For information on sexually transmitted diseases visit the website
-
Lab tests online
For more information on specific exams visit the website